The measure concrete slump test is a fundamental procedure in construction that evaluates the workability and consistency of fresh concrete. This simple yet effective test helps determine the ease with which concrete can be mixed, placed, and compacted. Properly measuring concrete slump ensures that the concrete will perform as expected once hardened, maintaining strength, durability, and stability. It is particularly useful for quality control on construction sites, providing immediate feedback on whether the mix meets the project specifications. A concrete mix that fails to meet slump requirements may require adjustments in water content, cement ratio, or aggregate proportions to ensure the intended performance of the structure.
Importance of Measuring Concrete Slump
Measuring concrete slump is essential because it directly influences the quality of the final structure. The slump indicates the water content and flow characteristics of the concrete mix, which are critical for proper placement and compaction. Concrete that is too stiff may not flow into formwork properly, creating voids and weak points, while overly wet concrete may lose strength and be prone to shrinkage cracks. By measuring concrete slump, engineers and workers can adjust the mix on-site to maintain workability without compromising structural integrity. It also helps in maintaining consistency between different batches of concrete, ensuring uniformity throughout the project.
Equipment Needed to Measure Concrete Slump
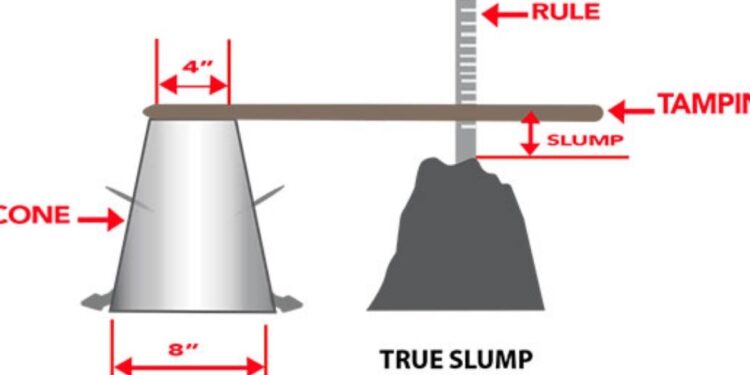
To accurately measure concrete slump, a few standard tools are required. The main equipment includes a slump cone, a tamping rod, a base plate, and a measuring scale. The slump cone is typically made of steel or aluminum and has a conical shape with specific dimensions. The tamping rod is used to compact the concrete within the cone to remove air pockets and ensure uniform density. The base plate provides a stable, non-absorbent surface for the cone during the test. Using the proper equipment ensures that the measure concrete slump test is accurate, repeatable, and compliant with standard construction practices.
Procedure to Measure Concrete Slump
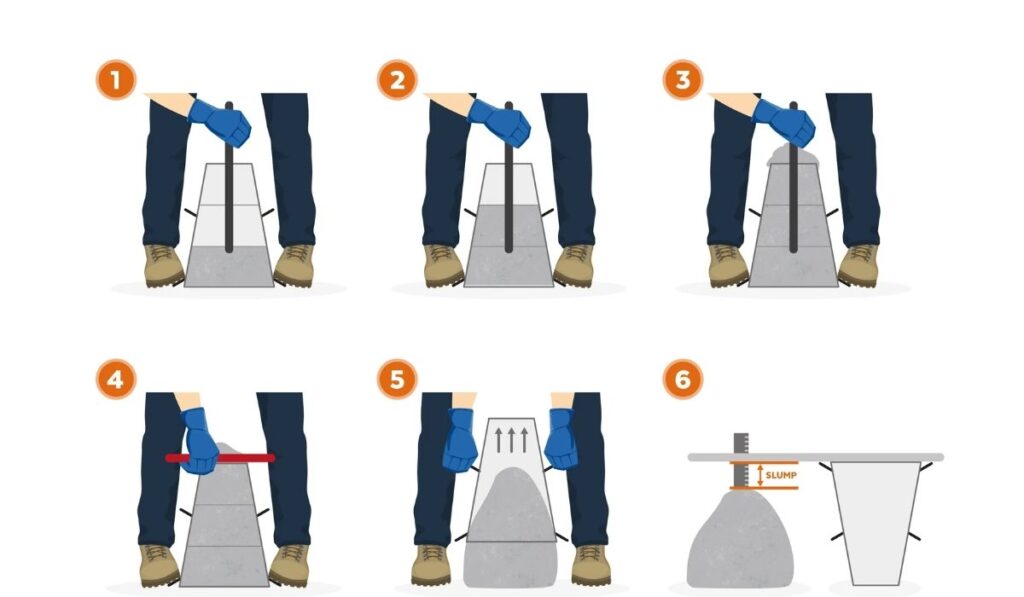
The procedure to measure concrete slump follows a standardized method to maintain consistency. First, the slump cone is placed on a stable, non-absorbent surface. Concrete is then poured into the cone in three layers, with each layer being tamped uniformly using the rod to remove air pockets. After filling and tamping the top layer, the cone is carefully lifted vertically without disturbing the concrete. The resulting change in height between the top of the cone and the top of the concrete indicates the slump. This difference is measured with a scale or ruler, giving the concrete’s slump value. Accurate measurement is crucial for determining whether the mix meets the specified workability requirements.
Factors Affecting Concrete Slump
Several factors influence the slump value when you measure concrete slump. The water-to-cement ratio is one of the most significant, as higher water content increases workability and slump, while lower water content results in a stiffer mix. Aggregate size, shape, and gradation also play an important role; rounded aggregates tend to increase slump, while angular aggregates decrease it. Admixtures, such as plasticizers or superplasticizers, can alter slump without changing water content. Temperature, mixing time, and handling practices further affect the slump value. Understanding these factors allows engineers to interpret the results correctly and make adjustments to achieve the desired concrete consistency.
Types of Slump Tests
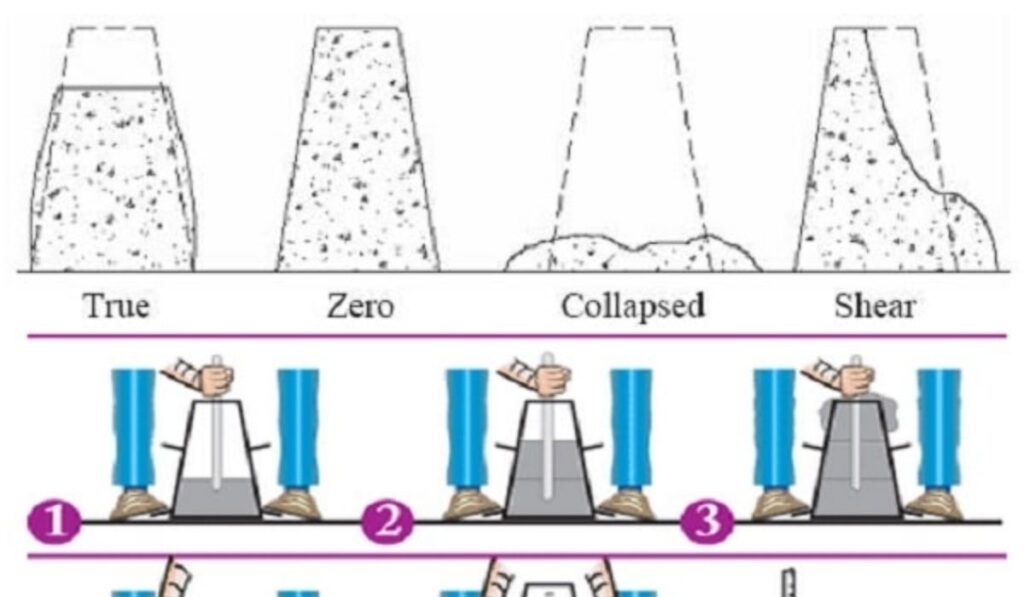
There are several variations of the slump test used to measure concrete slump based on the behavior of the concrete during the test. The standard test measures the vertical settlement of the concrete, but modified versions include the true slump, shear slump, and collapse slump. A true slump occurs when the concrete subsides evenly while maintaining shape. Shear slump involves a tilting or shearing of part of the concrete, indicating excessive moisture or uneven aggregate distribution. Collapse slump occurs when the concrete collapses completely, signaling an overly wet mix. Each type provides insight into the properties of the concrete and whether adjustments are needed for proper placement.
Applications of Slump Test in Construction

The ability to measure concrete slump is vital across various construction projects, from residential buildings to large infrastructure projects. It ensures that concrete used in foundations, beams, columns, slabs, and pavements has the appropriate workability for placement and compaction. Slump testing is particularly important for ready-mix concrete deliveries, where maintaining consistency between batches is critical. Contractors rely on slump measurements to verify compliance with specifications and to make immediate adjustments if the concrete mix is too stiff or too fluid. This ensures structural safety, durability, and long-term performance.
Limitations of Measuring Concrete Slump
Although measuring concrete slump is a reliable method for assessing workability, it has limitations. The test does not directly measure strength, durability, or long-term performance of concrete. Variations in operator technique, surface conditions, and cone handling can affect results. The slump test is most useful for medium to stiff concrete mixes; highly fluid mixes or very dry mixes may yield inconsistent results. Understanding these limitations is essential for interpreting slump values correctly and using them alongside other quality control measures, such as compressive strength tests and mix design verification, to ensure overall concrete performance.
Best Practices When Measuring Concrete Slump
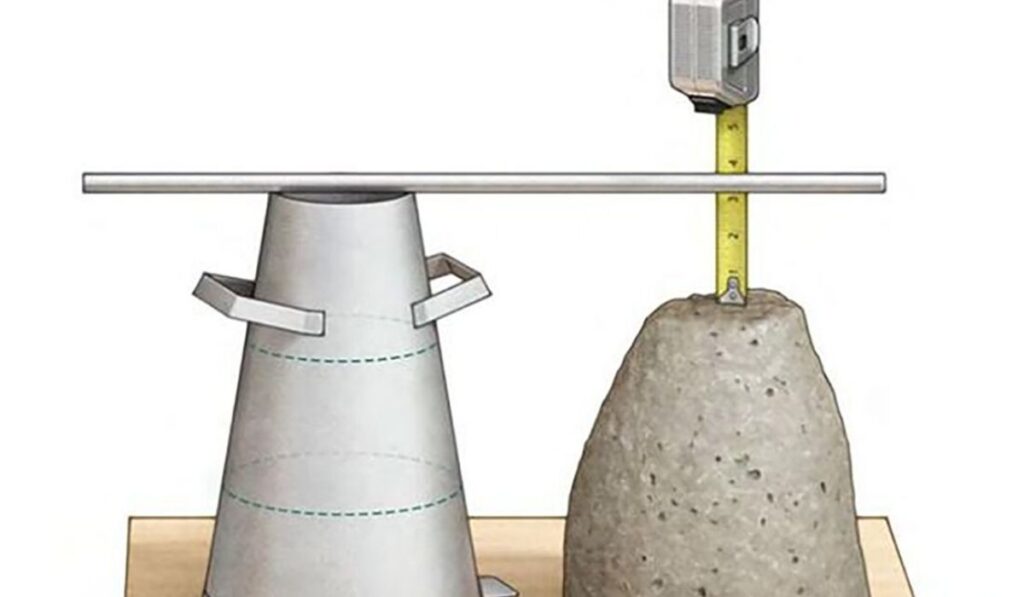

To ensure accurate results when you measure concrete slump, certain best practices should be followed. The surface must be level and non-absorbent, and the cone should be lifted vertically without twisting. Uniform tamping for each layer ensures proper compaction and avoids air pockets. Concrete should be fresh, mixed properly, and tested immediately after mixing to avoid changes in moisture content or workability. Documenting results for each batch helps maintain consistency across the project. Following these practices reduces errors and provides reliable data for evaluating concrete performance on-site.
Final Thoughts
Frequently Asked Questions
Measuring concrete slump is a critical quality control procedure in construction that provides immediate insights into concrete workability and mix consistency. By using proper equipment, following standardized procedures, and understanding factors affecting slump, engineers and contractors can ensure concrete meets specifications for placement and durability. The measure concrete slump test remains an essential tool for maintaining the structural integrity and performance of concrete structures. For further technical details, explore measure concrete slump.
1. What is the purpose of measuring concrete slump?
- It determines the workability and consistency of fresh concrete
2. What equipment is needed to measure concrete slump?
- Slump cone, tamping rod, base plate, and measuring scale
3. What factors affect the slump value?
- Water-to-cement ratio, aggregate type, admixtures, and handling practices
4. Can slump indicate concrete strength?
- No, slump only measures workability, not strength or durability
5. How can accuracy be ensured when measuring concrete slump?
- Use proper procedure, fresh concrete, uniform tamping, and a level surface